TM 5-3805-290-23-1
THEORY OF OPERATION - CONTINUED
0003 00
ENGINE - CONTINUED
5.
Connecting Rods.
a.
Connecting rods are machined from forged molybdenum steel. Connecting rod has a small, wedged-shaped end.
b.
Mating surface of bearing cap and connecting rod is made by serrations in both bearing cap and connecting rod.
Bearing cap is mounted to connecting rod by two bolts and two nuts.
c.
Engine is equipped with connecting rods that have a fracture split cap. Fracture split caps are retained with torx
screws. Connecting rods that are fracture split have higher rod integrity and improved strength due to splitting,
which produces an accurately matched surface on each side.
6.
Crankshaft.
a.
Crankshaft is a chromium molybdenum forging. Crankshaft has seven main journals.
b.
Crankshaft end play is controlled by two half-thrust washers located on both sides of center main bearing.
c.
Main bearings are made with a steel back and a bearing material. Bearing material is an alloy of aluminum and tin.
Exception is center main bearing, which is lead bronze with a lead finish. Main bearing caps are made of cast iron
or spheroidal graphite (SG) iron.
7.
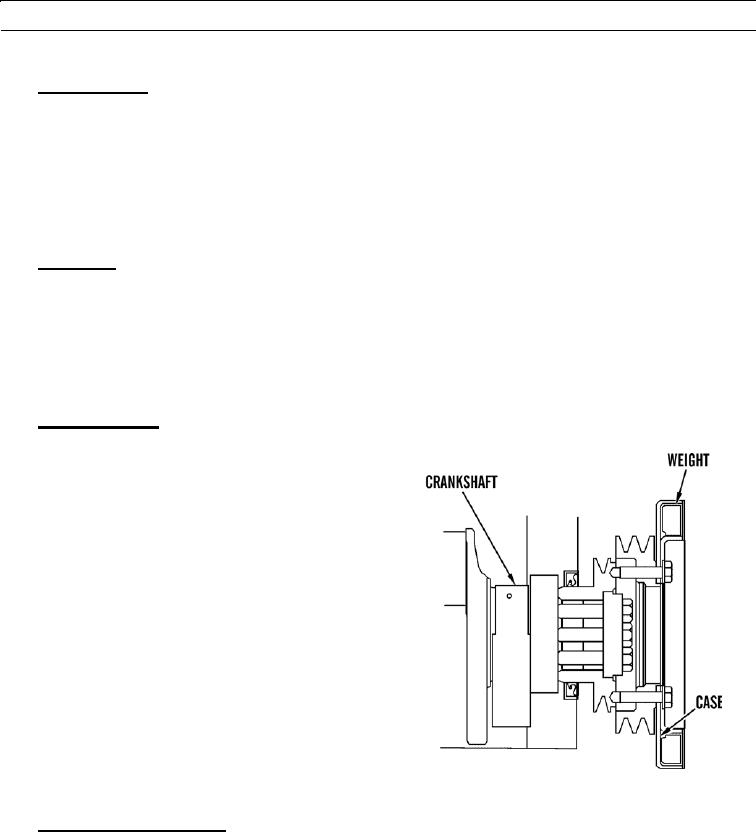
Vibration Damper.
Force from combustion in cylinders will cause crank-
shaft to twist. This is called torsional vibration. If vibration is
too great, crankshaft will be damaged. Vibration damper lim-
its torsional vibration. Vibration damper is designed as a vis-
cous damper. Space between weight and case is filled with
viscous fluid.
427-B1502
8.
Gears and Timing Gear Case.
a.
Timing case is constructed of either aluminum or cast iron. Aluminum timing case cover contains front oil seal.
b.
Timing gears are made of steel or cast iron.
c.
Crankshaft gear drives upper idler gear and lower idler gear. Upper idler gear drives camshaft and fuel injection
pump. Lower idler gear drives oil pump. Water pump is driven by fuel injection pump gear.
d.
Camshaft and fuel injection pump rotate at half engine speed.
0003 00-2

