TM 5-3805-290-23-1
THEORY OF OPERATION - CONTINUED
0003 00
AIR CONDITIONING SYSTEM - CONTINUED
Refrigerant Compressor
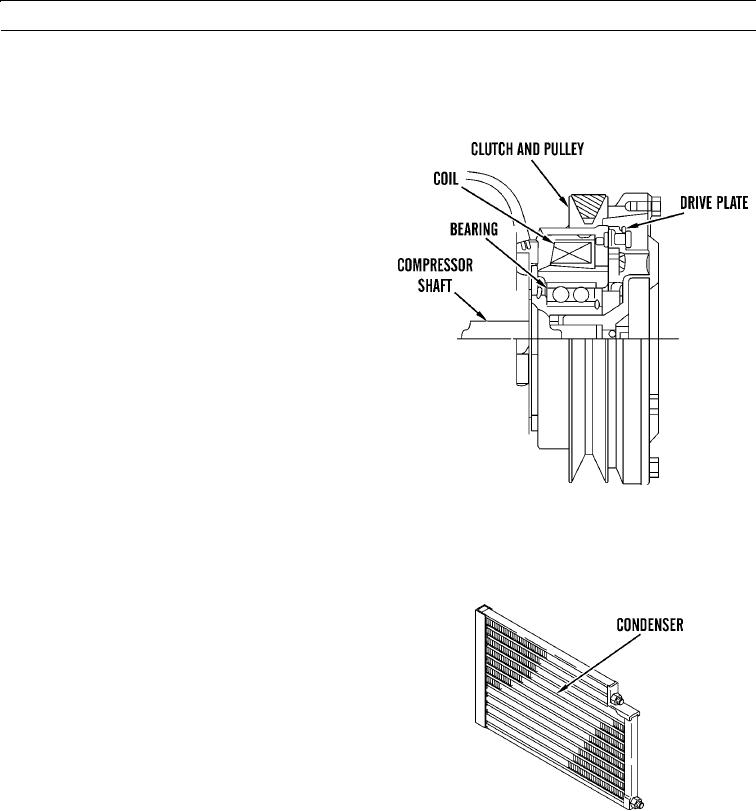
1.
The compressor is driven by the engine. A belt con-
nects the engine to the clutch and pulley assembly.
The pulley is located on the clutch. The drive plate is
fastened to the shaft of the compressor. The clutch and
pulley assembly turns on the bearing. The clutch and
pulley assembly are not connected to the shaft. The
electric current from the thermostat controls a mag-
netic field in the coil assembly.
2.
The magnetic field pulls the drive plate against the
clutch and pulley assembly. The clutch and the pulley
assembly turns the shaft that operates the compressor.
When the current to the coil assembly is stopped, the
magnetic field is removed. This allows the drive plate
to move away from the clutch and pulley assembly.
The clutch and the pulley assembly will turn freely on
the bearing. The sequence of connecting and discon-
necting the pulley to the compressor shaft is called
compressor cycling. The compressor cycling is con-
trolled by the thermostat. The thermostat is controlled
427-B2085
by the capillary tube, which is installed between the
fins of the evaporator coil.
Refrigerant Condenser
1.
When the refrigerant leaves the compressor, the refrig-
erant is a vapor. The temperature of the refrigerant is
high and the pressure of the refrigerant is high when
the refrigerant leaves the compressor. The increase in
pressure of the refrigerant causes an increase in tem-
perature of the refrigerant. The refrigerant vapor
leaves the compressor and the refrigerant enters the
condenser.
2.
The refrigerant must be converted into a liquid that
has high temperature and high pressure. The refriger-
ant must be converted into a liquid in order to increase
427-B2086
the efficiency of the air conditioning system. The con-
denser converts the refrigerant vapor into a liquid that
has high temperature and high pressure.
3.
When the refrigerant vapor leaves the compressor, the refrigerant vapor enters the condenser. The condenser is in a loca-
tion that is exposed to outside air. In order to convert the refrigerant into a liquid, the refrigerant must lose heat. The
refrigerant must reach the temperature of saturation. At the temperature of saturation, the refrigerant vapor will become
a liquid. The temperature of saturation of the refrigerant depends on the pressure of the refrigerant.
0003 00-195

