TM 5-3805-258-24-1
E L E C T R I C A L T R O U B L E S H O O T I NG
9 5 0 B O P E R A T O R ’ S S T A T I ON
DIODES
Several silicon diodes are used in the electrical system. The purpose of a diode
is to permit the flow of current in one direction but not in the other direction.
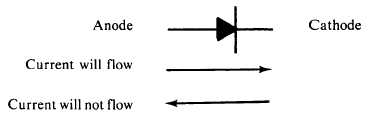
Diodes are shown in schematics as:
NOTE: The shape of the diode symbol is an indication of the direction that
current can flow.
The identification of the diodes used in this system can be made from the
drawing that follows. The end with the band is the cathode.
The diodes are of two types. The 2V9473 Diode Assembly has type 1N4004
(not a Caterpillar Part No.) Diodes. They have a capacity of one ampere
maximum current in the forward direction and 600 volts maximum reverse
voltage. The 1V9633 Diode Assembly has type 1N5405 (not a Caterpillar Part
No.) Diodes. They have a capacity of 30 amperes maximum current in the
forward direction and 400 volts maximum reverse voltage.
On the 950B, diodes are used for the purposes that follow:
1.
2.
Reverse Polarity Protection
Make reference to “Main Power Circuit” drawing, “C” in that circuit is used
to prevent the operation of the main power relay Diode if the batteries are
installed in the reverse direction by accident. If the main power relay were
activated with the batteries in the reverse direction, damage to the alternator
would be the result.
In this circuit the diode sends current constantly during normal operation. It
prevents the flow of current only if the batteries are installed in a reverse
direction.
Freewheeling or Flywheel Effect
Several circuits have relay coils or solenoids. Both of these have electrical
inductance. The effect of electrical inductance is to have a resistance to
change (either increase or decrease) in the amount of current that flows
through it. As an example, if a constant current flows through an inductance
(coil) and a switch in the circuit is suddenly opened, the inductance (coil)
makes a resistance to the sudden decrease in current. It becomes a strong
source of voltage for a very short time. The voltage caused by the inductance
can be much greater than the voltage of the battery. An arc is caused at the
switch for a short time until the energy in the inductance is gone. Damage to
the switch can be the result.
4-137